CHANGING HOW THE WORLD THINKS ABOUT AGING
Science-backed solutions restoring critical metabolites for healthier, longer lives.

The propion Mission
Propion was founded to tackle one of the most overlooked drivers of aging: dysregulated tryptophan metabolism. Our mission is to create products that address aging at its root, guided by real science not trends.
THE PROPION AXIS
Our research focuses on Propion Molecules - Powerful gut-derived metabolites that protect the brain, gut, and mitochondria. By restoring these molecules, we aim to extend healthspan and vitality.
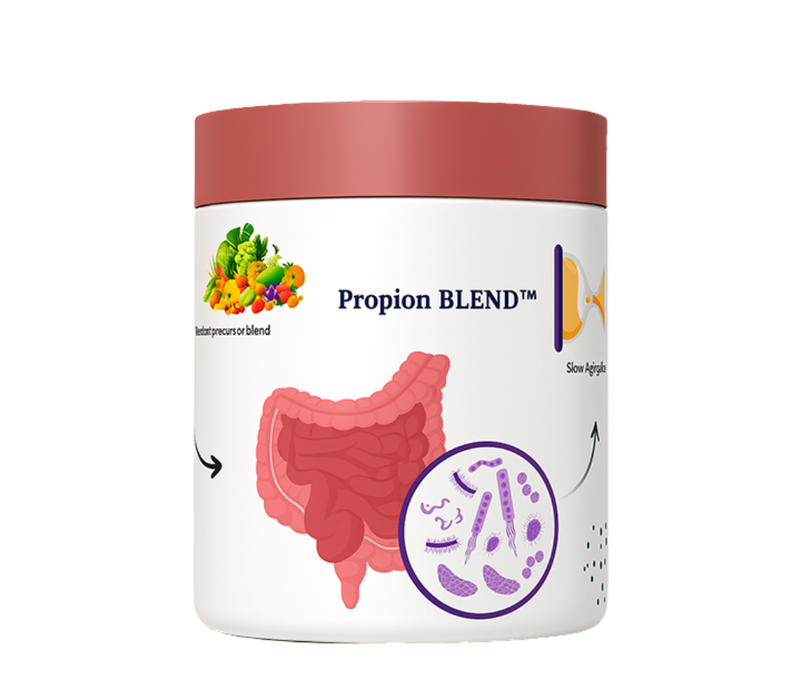
Propion BLEND™
-
Developed over 20 years of research
-
Backed by leading experts in aging, gut health, and nutrition
-
Clinically shown to double powerful anti-aging gut metabolites over 12 months
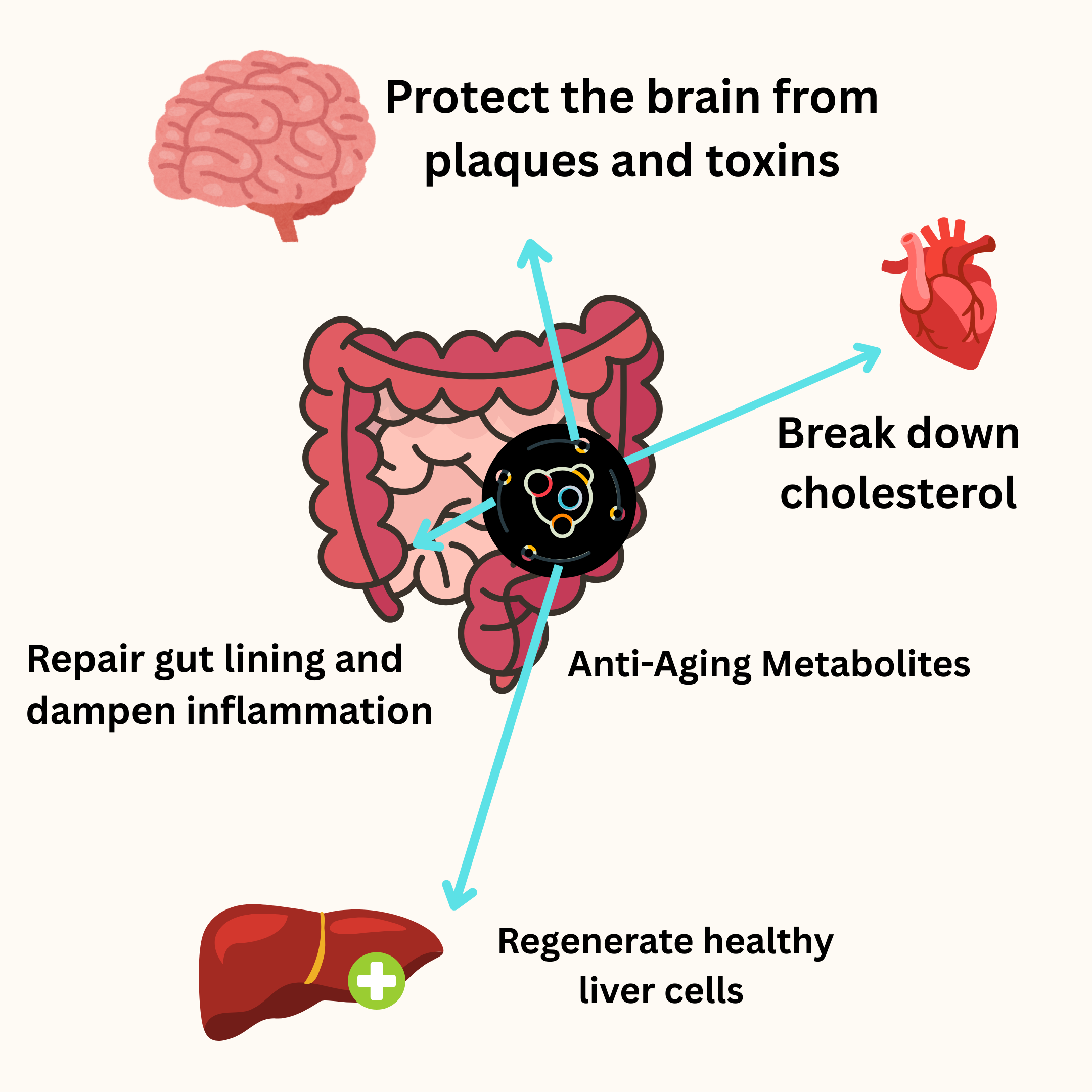
SCIENCE FIRST. RESULTS THAT LAST.
Unlike trendy supplements, every Propion product is built on peer-reviewed science, developed by world-class researchers, and designed for long-term impact.





